Abstract: We have installed the Blockstream Bitcoin Satellite system, a way to download and verify Bitcoin’s blockchain via satellite, without the need for an internet connection. We were able to set up the system reasonably quickly and the satellite connection does indeed have enough bandwidth to keep the node at Bitcoin’s tip, most of the time. We conclude by establishing that although many Bitcoin enthusiasts are likely to find installing and running the system enjoyable, it is unlikely to serve any practical purpose for most users. However, because this satellite based system does have the potential to improve the censorship resistance characteristics of the Bitcoin network and defend against some forms of eclipse attacks, its existence is probably a positive development.

Overview
Following on from our experimentation with Bitcoin miners a few weeks ago, in this piece we install and use the “Bitcoin Satellite”, a product supplied by Blockstream. We ordered the Blockstream Satellite Pro Kit and Blockstream’s Flat-Panel Antenna, quite an expensive package, priced at almost US$1,200 in total.

Installation
The installation process was easier than we expected and only took a few hours. Essentially all one needs to do is install the satellite dish, point it in the right direction, connect it to a laptop running Linux and run some custom Blockstream software, along with a modified version of Bitcoin Core 0.19.1. The most challenging part was the alignment of the dish to the geostationary satellite, however once we worked out how to effectively use the alignment tool (by adjusting the sensitivity), it only took around 15 minutes to align. However, the weather conditions were favourable and this could have been more challenging in different conditions.


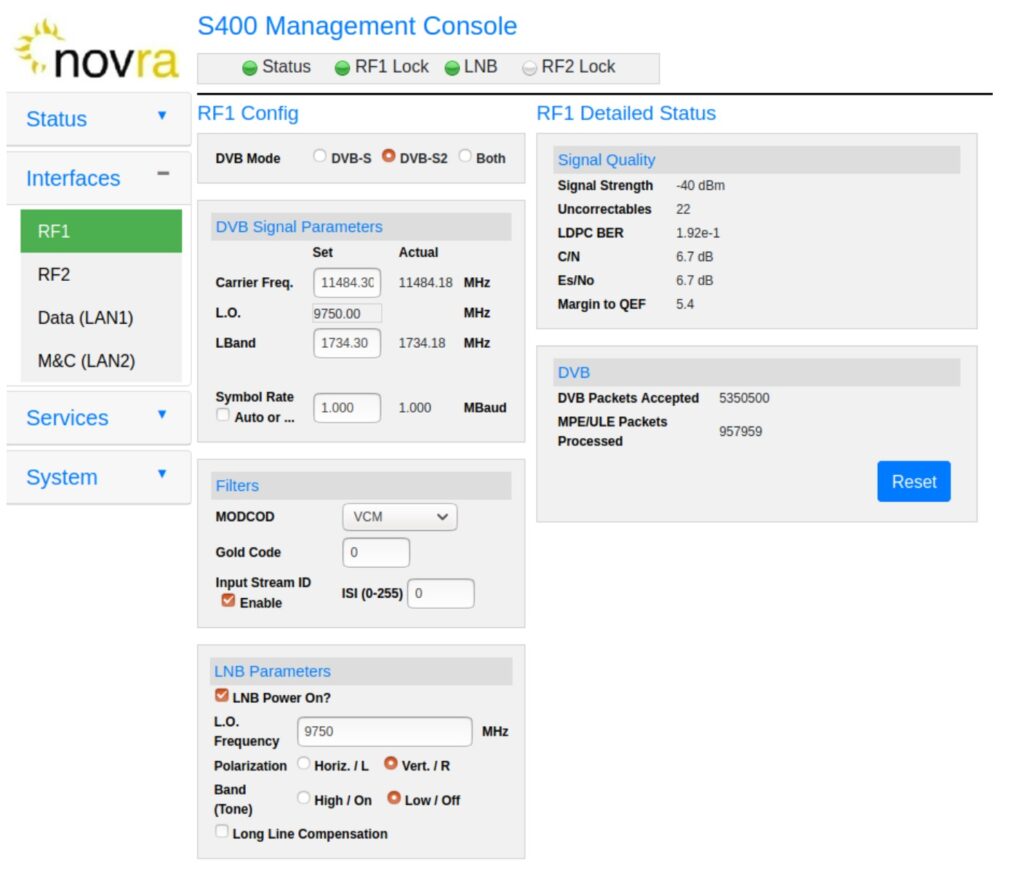
Usage
We synced the Bitcoin node to the current tip using the internet and once the tip was reached, we disabled the internet connection by adding connect=0 to the Bitcoin configuration file. After this, to verify the Bitcoin P2P network was not functioning, we confirmed that the client did not have any peers.
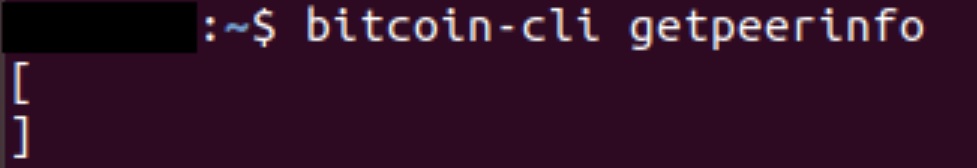
The satellite node was then able to function and stay at the tip by receiving the Bitcoin blocks via satellite. Typically, the node learnt about a block 5 to 10 seconds after our internet based nodes found out about them. The node then downloaded and verified the blocks in full, around 2 minutes behind the internet based nodes. However, please note that our experience is very limited and we have only been using the satellite based node for a few days.
The client downloads the blocks in chunks, firstly the block header in chunks, followed by the main body of the block, again in chunks. Based on the way the satellite broadcasts the block data, the node does not always download blocks in a continuous order and is able to fill the gaps of missing blocks later on.
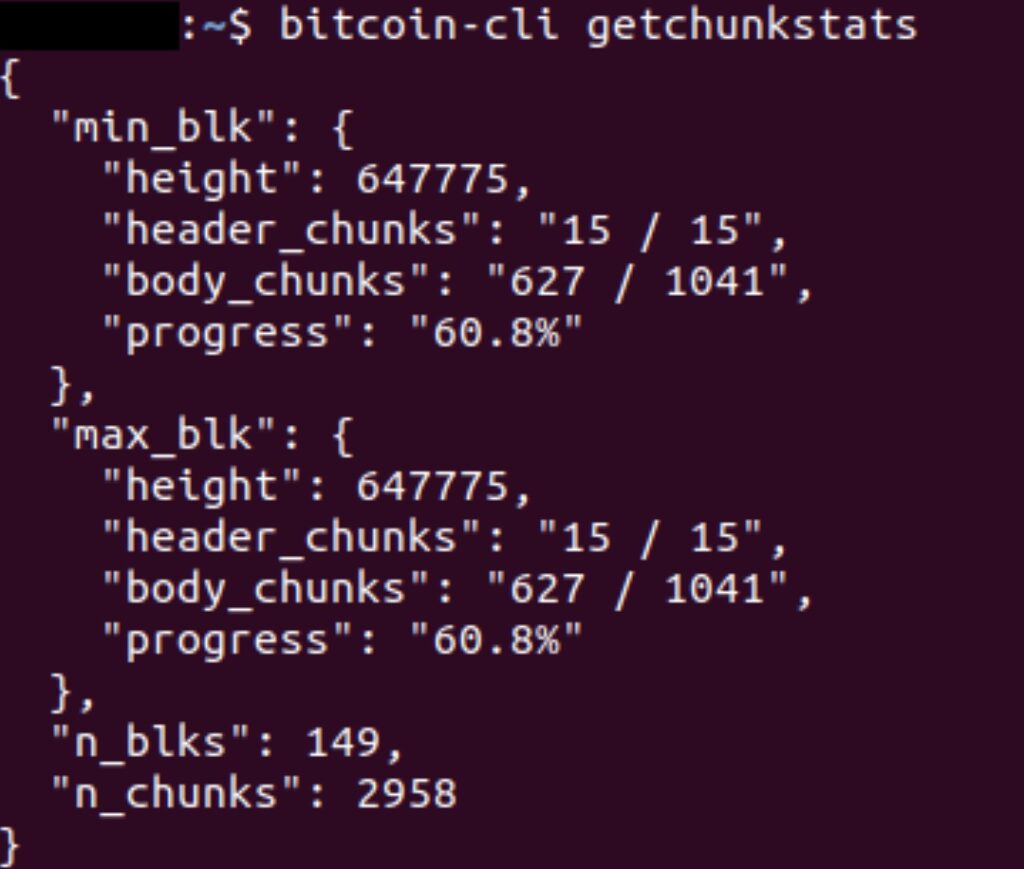
On occasions the satellite node was unable to keep up with the chaintip and fell a few blocks behind. Based on the speed of our satellite connection, once it was 4 to 5 blocks behind it often struggled to catch back up to the chain tip.
Fork Monitor
We added our satellite node to the Fork Monitor website. The node can be identified by the satellite receiver emoji and one can track how the node performes compared to the internet based nodes. It often gets stuck or lags by a few blocks, but most of the time it is at the chain tip.
(ForkMonitor.info)
Monitoring the satellite node may be of interest as we can establish how the satellite feed reacts in the event of a stale block or chainsplit.
Conclusion
Installing and running the satellite based Bitcoin node was enjoyable. This product is certainly worth it for a certain type of Bitcoin geek, just for the fun of it really. As for whether it is useful, we are a bit doubtful. It is probably highly unlikely that one will be in a circumstance where:
i. You need to use Bitcoin by syncing the chain,
ii. You don’t have a working internet connection, and
iii. You have all the necessary equipment and are able to get the satellite feed working to sync to your incoming transaction.
The counter argument to this is that the system improves the censorship resistance properties of the network. For instance if potential users are in remote locations in jurisdictions with highly restrictive internet censorship. In this scenario, we can see how a potential user could install the satellite system and fully verify incoming payments. Another potential advantage of the satellite setup is that, although the broadcasts are centrally controlled by Blockstream, it can be thought of as an independent check, which can help mitigate the risk of someone attempting some form of eclipse attack. This project is therefore commendable, in our view.
Related
The post appeared first on Blog BitMex